Welcome to our Carnivore / Ketovore / Keto Online Community!
Welcome to Carnivore Talk! An online community of people who have discovered the benefits of an carnviore-centric ketogenic diet with the goal of losing weight, optimizing their health, and supporting and encouraging one another. We warmly welcome you! [Read More]
- Replies 8
- Views 1.6k
- Created
- Last Reply
Top Posters In This Topic
-
Bob 2 posts
-
Orweller 1 post
-
1958MaleInEngland 1 post
-
Carnivore Club 1 post
Most Popular Posts
-
The self decode link reads like medical propaganda. More sick people = more Big Pharma money. They want us all vegan.
-
Welcome Sephiroth. I dig the name, as I am currently playing Final Fantasy 7 Rebirth 😄 I'm going to copy and paste your list and replace your comments with mine... 1. Fiber -Not needed, like
-
1. Fiber - Not needed, however, it won't hurt you to get small amounts in case, I do it myself, about 5 to 8 grams a day. 2. Probiotics/Prebiotics - I take probiotics. 3. Butyrate/Butyric acid - N
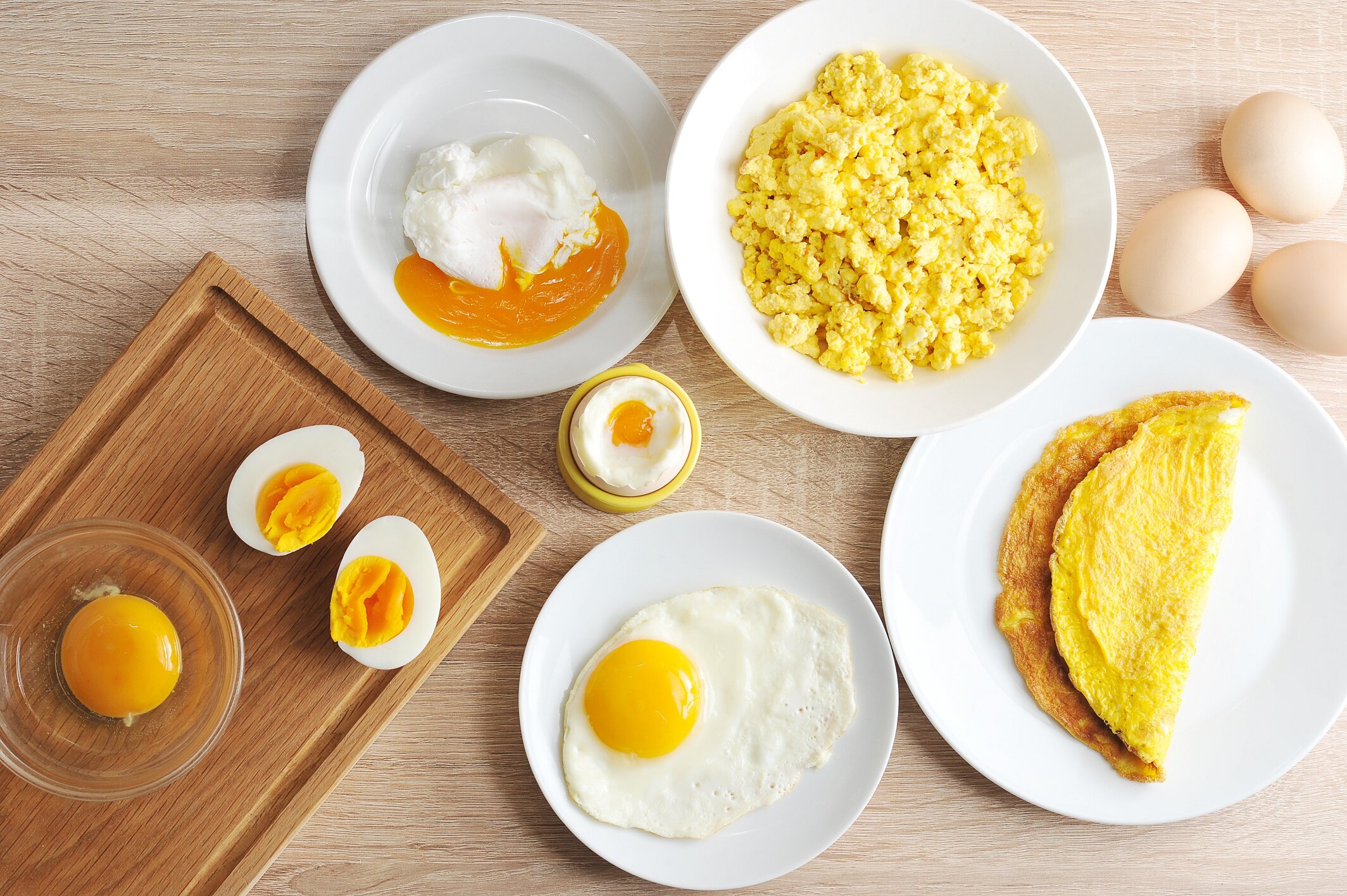







I am planning to start carnivore. I am 6 feet and close to 300 lbs. After adjusting to new fuel source I might go back to training powerbuilding. What about supplementation? People claim that supplements are not needed. But I want to ask separately about each supplement:
1. Fiber - I think that fiber might not be needed on carnivore.
2. Probiotics/Prebiotics - I think they are not needed on carnivore.
3. Butyrate/Butyric acid - Would it be useful or would I get it enough on the diet.
4. BHB Ketones supplement - Would I benefit from it during transition process and after or is it worthless? I heard/read that it might be good together with Butyrate/Butyric acid.
5. Methylsulfonylmethane - not sure about this supplement. Should I take it or will I get it from diet or is it not needed?
6. Glucosamine - not sure about this supplement. Should I take it or will I get it from diet or is it not needed?
7. Collagen - should I supplement it or will I get enough from diet (bone broth)?
8. Glycine - should I supplement it or will I get enough from diet (bone broth)?
9. Q10 - should I supplement it or will I get enough of it from meat (heart)?
10. Minerals - this one might be needed especially in the beginning but will it be needed later into diet?
11. Omega 3s - I think it might not be needed on carnivore.
12. Vitamin A - I think it might not be needed.
13. Vitamin B (group) - I think it might not be needed.
14. Vitamin C - not sure. People say that due to not consuming carbs carnivores need less of it.
15. Vitamin D (+ K) - should I supplement vitamin D or D+K or none? Some supplement only with D but some say that D needs K so they supplement together. But on carnivore I should have enough K. But I am not sure is having enough is the same as taking them together. Some argue they must be taken together, is that true? If yes would I need to take D while eating food with K or better take both in supplement form or I need none in supplement form?
16. Vitamin E - the stupidest one for me. There are tocopherols and tocotrienols. Although body stores a-tocopherol but some newer research proven that tocotrienols are better and tocopherols are bad/worse compared to tocotrienols and that (too much) tocopherols can reduce/hinder good potential from tocotrienols. So should I take tocotrienols and avoid tocopherols or no supplementation of any vitamin E form is needed. Also I read that vitamin E reacts with vitamin K and is antagonist of vitamin K; that vitamin K thickens blood and vitamin E thins blood. Not sure what to think about it. Are antioxidants that needed on carnivore?
17. https://health.selfdecode.com/blog/carnivore-diet/ What you think about this?
18. Geranylgeraniol - what is that? Should it also be supplemented? It is often mentioned with Q10 and vitamin E. Is it antioxidant?