Welcome to our Carnivore / Ketovore / Keto Online Community!
Welcome to Carnivore Talk! An online community of people who have discovered the benefits of an carnviore-centric ketogenic diet with the goal of losing weight, optimizing their health, and supporting and encouraging one another. We warmly welcome you! [Read More]
Agriculture Created a Nightmare for Our Teeth
- Replies 3
- Views 6.8k
- Created
- Last Reply
Popular Days
Most Popular Posts
-
The work of Weston Price also showed that indigenous people who ate primarily meat had super healthy teeth and jawbones.
-
This is fascinating. Recently I’ve been hearing bits and pieces here and there of dental hygiene and carnivore. Dr. Chaffee has mentioned it several times. I’ve heard some carnivores talk about going

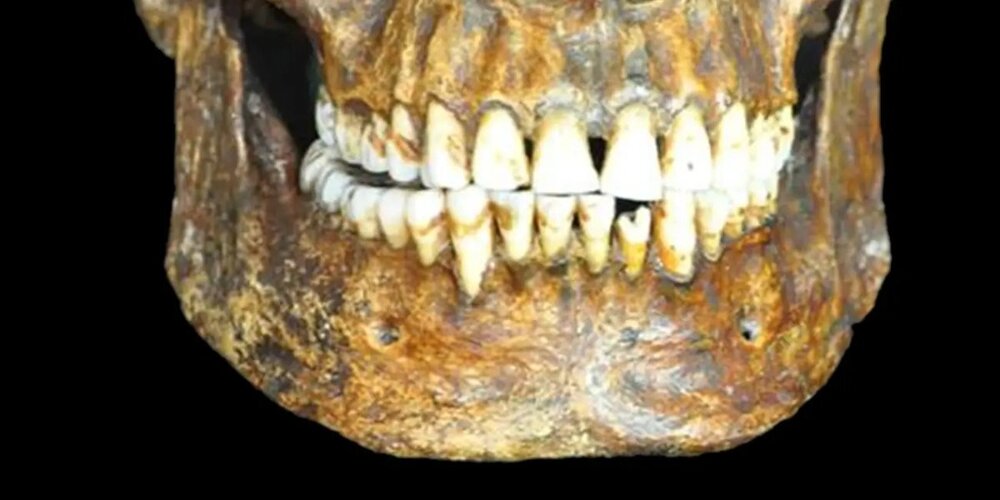





Agriculture is the bedrock of civilization but created a nightmare for our teeth
The agricultural revolution changed everything, and it's tough to overstate this fact.
No longer tethered to roaming animal herds, or reliant on foraged berries, learning to grow our own food some 10,000 years ago allowed (and forced) us to settle down.
But that crucial Neolithic shift came with a cost that haunts humanity to this day: It devastated our teeth.
Farming grains and other carbohydrate-rich foods freed up a lot of time for our ancestors. In turn, this helped spur the development of culture, art, trade, science, and all the other things that go into complex human civilization (like news sites you read on the internet).
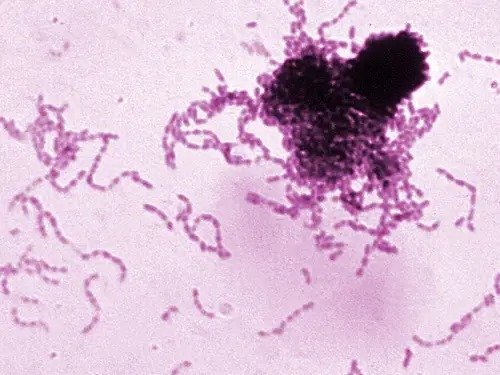
Yet this flood of carbs made our mouths — long-adapted to a more complex diet — a fertile breeding ground for one type of bacteria called Streptococcus mutans.
S. mutans is most commonly associated with cavities and tooth decay. It feeds off the carbs, including sugars, that get stuck in our teeth, metabolizing them into lactic acid. This acid then eats away at dental enamel and rots our teeth.
The bacteria is basically built for the human mouth, and is passed down from mothers to children during infancy.
However, our teeth hadn't really evolved to deal with it in large numbers, and researchers used genetics to discover that, around 10,000 years ago, S. mutans started to grow exponentially — right in time with the rise of agriculture.
After that first Neolithic bump for S. mutans, bacterial diversity in the human mouth pretty much remained consistent through the Middle Ages.
Our initial switch to farming wasn't the only time we gave a boost to S. mutans, though. During the Industrial Revolution 150 years ago, another major agricultural shift occurred: We introduced an enormous amount of processed flour and sugar into our diets.
This lit the powder keg we'd built for S. mutans, helping it crowd out other bacteria species to become the dominant dental bacteria, form stubborn and gnarly plaques of biofilm, and more rapidly chew away at our teeth.
ARTICLE SOURCE: https://www.businessinsider.com/growing-crops-human-cavities-increase-2016-3
Subscribe to Carnivore Talk on YouTube | Be our guest on the channel | Leave me a voicemail, yo!