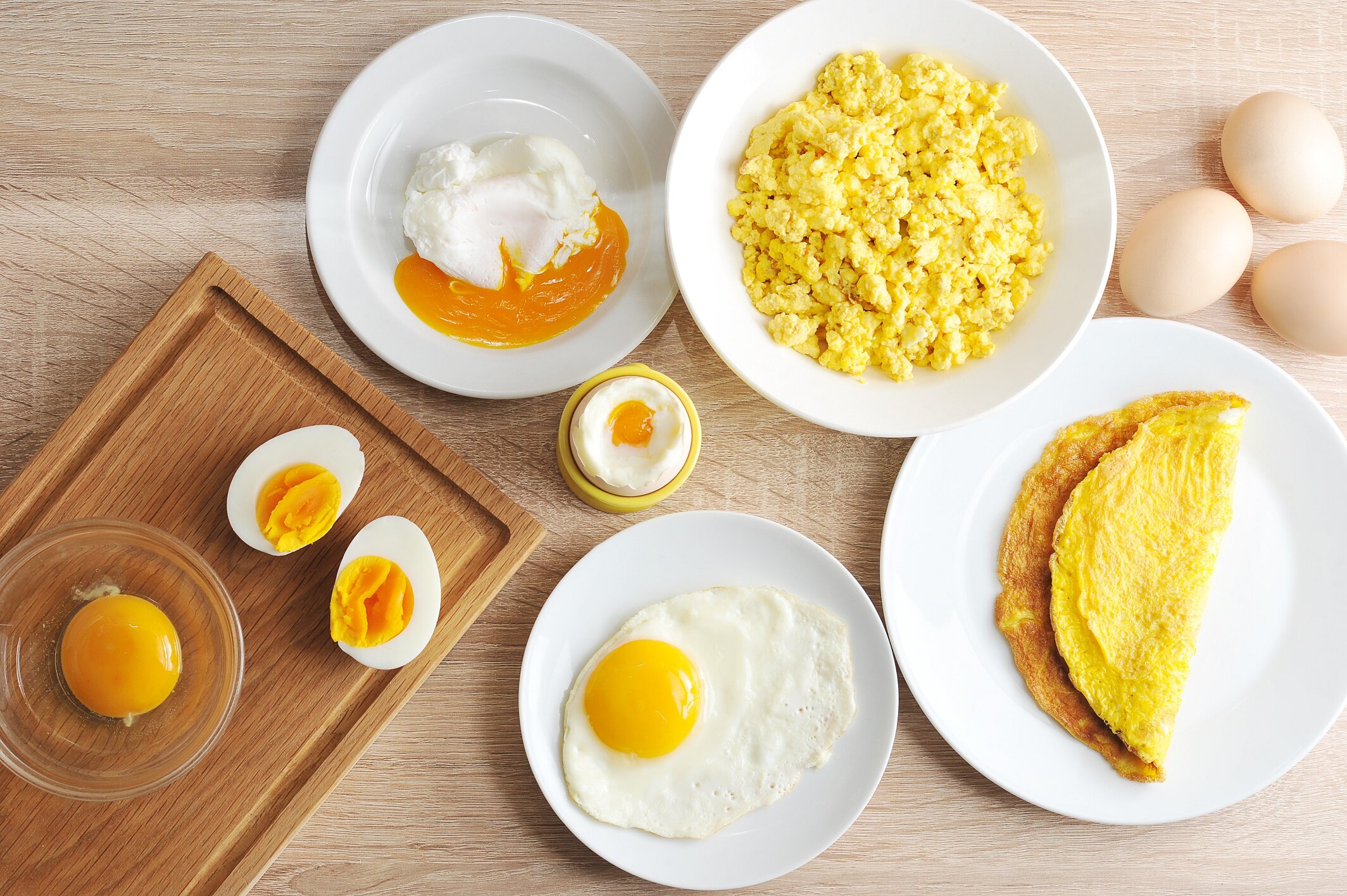
New study shows some plant-based diets may raise heart disease riskSummary: Researchers tracking over 63,000 adults found that high-quality, minimally processed plant foods significantly reduce cardiovascular risk. But when those plant foods are ultra-processed, the advantage disappears—and can even backfire. Some ultra-processed plant diets increased risk by 40%. The study urges a shift toward whole, naturally nutrient-rich plant foods. FULL STORY Not all plant-based diets improve heart health—only those built on minimally processed, nutrient-dense foods do. Ultra-processed plant products can erase the benefits and even increase cardiovascular risk. Credit: Shutterstock Previous studies have indicated that eating large amounts of ultra-processed foods[1] is linked with a higher likelihood of developing cardiovascular diseases. Other research[2] has found that diets centered on plant-based foods can lower this risk when those foods offer balanced nutrition and are consumed in appropriate proportions. To explore how nutrition relates to cardiovascular health in more detail, scientists from INRAE, Inserm, Université Sorbonne Paris Nord, and Cnam examined more than whether foods came from plant or animal sources. Their assessment also incorporated the nutritional makeup of foods, including factors such as carbohydrate, fat, and antioxidant vitamin and mineral content, along with the level of industrial processing involved. How the Study Evaluated Diets and Food Choices The team evaluated data from 63,835 adults enrolled in the French NutriNet-Santé cohort. Participants were followed for an average of 9.1 years, with some tracked for as long as 15 years. Information on what they ate and drank (collected over at least three days) was gathered through online questionnaires. This detailed approach allowed researchers to classify diets based on the share of plant-based and animal-based foods, while also considering both nutritional quality and processing level. The findings showed that adults who consumed more plant-based foods of higher nutritional quality (lower in fat, sugar, and salt) and with minimal industrial processing had about a 40 percent lower risk of cardiovascular disease compared with those who ate fewer nutritious plant-based foods and more animal-based products[3]. However, people who ate larger amounts of plant-based foods that were nutritionally higher quality but ultra-processed, including items such as industrial whole meal breads, store-bought soups, ready-made pasta dishes, or commercially prepared salads with dressing, did not experience a reduced cardiovascular risk relative to individuals who consumed fewer of these products and more animal-based foods. Ultra-Processed Plant Foods and Increased Heart Disease Risk A notably higher risk emerged for adults whose diets were dominated by plant-based foods that were both lower in nutritional quality and ultra-processed. These items included crisps, sweetened fruit drinks or sodas made from plant extracts, chocolate-based sweets or confectionery, sugary breakfast cereals, and savory biscuits. Their cardiovascular disease risk was roughly 40 percent higher than that of people who consumed more plant-based foods of good nutritional quality with little or no industrial processing. Why Processing Level Matters for Plant-Based Eating Overall, the results show that understanding the relationship between diet and cardiovascular health requires considering the nutritional quality of foods and how heavily they are processed, in addition to the balance of plant-based and animal-based components. These findings support public health recommendations that encourage the consumption of plant-based foods that are both nutritionally high quality and minimally processed (such as fresh, frozen, or high-quality canned fruits and vegetables without added fats, salt, sugar, or additives). Notes [1], [2], and [3] can be read at the article source.... ARTICLE SOURCE: https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2025/12/251214100928.htm







FDA Clears First Over-the-Counter Continuous Glucose Monitor
Today, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration cleared for marketing the first over-the-counter (OTC) continuous glucose monitor (CGM). The Dexcom Stelo Glucose Biosensor System is an integrated CGM (iCGM) intended for anyone 18 years and older who does not use insulin, such as individuals with diabetes treating their condition with oral medications, or those without diabetes who want to better understand how diet and exercise may impact blood sugar levels. Importantly, this system is not for individuals with problematic hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) as the system is not designed to alert the user to this potentially dangerous condition.
“CGMs can be a powerful tool to help monitor blood glucose. Today’s clearance expands access to these devices by allowing individuals to purchase a CGM without the involvement of a health care provider,” said Jeff Shuren, M.D., J.D., director of the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health. “Giving more individuals valuable information about their health, regardless of their access to a doctor or health insurance, is an important step forward in advancing health equity for U.S. patients.”
The Stelo Glucose Biosensor System uses a wearable sensor, paired with an application installed on a user’s smartphone or other smart device, to continuously measure, record, analyze and display glucose values in people 18 years and older that are not on insulin and who do not have problematic hypoglycemia. Users can wear each sensor up to 15 days before replacing with a new sensor. The device presents blood glucose measurements and trends every 15 minutes in the accompanying app. Users should not make medical decisions based on the device’s output without talking to their healthcare provider.
Data from a clinical study provided to the FDA showed that the device performed similarly to other iCGMs. Adverse events reported in the study included local infection, skin irritation and pain or discomfort.
As part of the Center for Devices and Radiological Health’s strategic priority to advance health equity, CDRH will continue to support innovation that addresses health equity by moving care and wellness into the home setting.
ARTICLE SOURCE: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-clears-first-over-counter-continuous-glucose-monitor
Subscribe to Carnivore Talk on YouTube | Be our guest on the channel | Leave me a voicemail, yo!