Welcome to our Carnivore / Ketovore / Keto Online Community!
Welcome to Carnivore Talk! An online community of people who have discovered the benefits of an carnviore-centric ketogenic diet with the goal of losing weight, optimizing their health, and supporting and encouraging one another. We warmly welcome you! [Read More]
- Replies 25
- Views 3.5k
- Created
- Last Reply
Top Posters In This Topic
-
Scott F. 13 posts
-
Terry 5 posts
-
Geezy 4 posts
-
ketomonster 2 posts
Most Popular Posts
-
🤣 that is a great explanation of what we do. I love it. 👍 And that is how it’s done. There has never been and will never be a true RCT of how we eat. And since we are all so individual we must be our
-
Maybe I progressed a bit fast, just not sure. But I read something similar and now I wonder if I am in the ravenous stage and the sugar is like a "150 shot of nitrous' on a drag car. Sometimes it is
-
Yep. My bag is not much more than a liter and it lands between $55k-$57K per bag. I hate to get all conspiracy-theorists and such, but this is why they need us to stay sick. LOL Scott



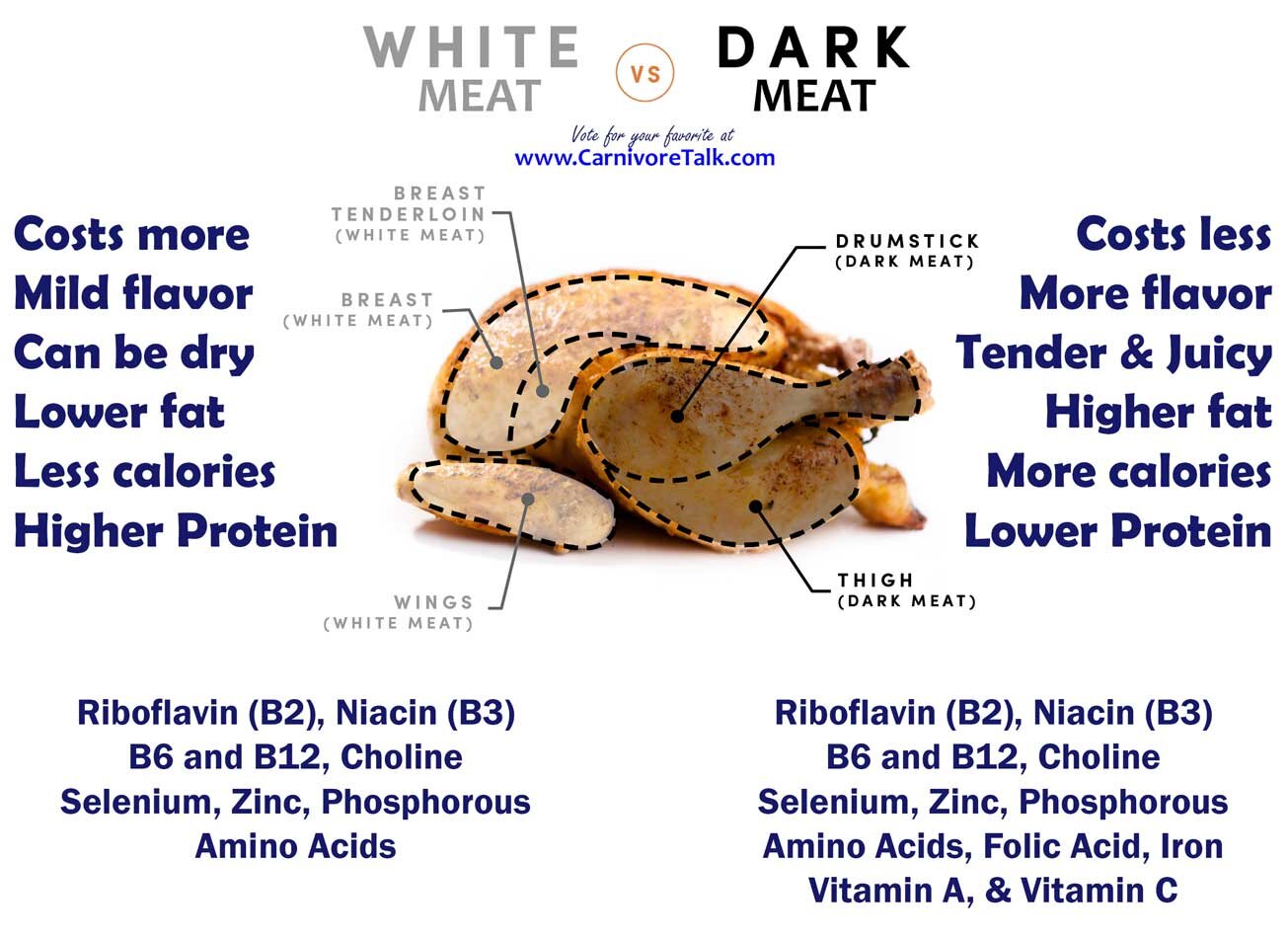


I have made note of carnivore, fasting and trying to hit protein targets. I have altered the fat content and found pretty much where I need to be.
I have also noted I am amazed by the amounts of food other people can eat in one setting. Once I get past a 3/4"-1" rib eye, I'm full and sometimes can manage to eat the other half of my wife's steak, but that can be a stretch. I have tried to hit protein targets as I am getting more and more into lifting at the gym.
The past few weeks I have been on a stretch of overtime. I am averaging just a tad over 66 hours per week. I have been using some of the time on nights to pursue my Google degree in Carnivore and my YouTube College of Medicine Certificate with a lot of the metabolic things that come along with the carnivore diet, fasting and lifting weights (with an autoimmune disease tossed in as well). I'm not close to graduating from either Google nor Youtube, but I am working on those degrees.
I read a ton on the sugar diet (not that I am interested but more so to read about the effects of sugar). I have read a ton on glucose, glycogen, the liver and the pancreas as well as insulin resistance and insulin sensitivity. Instead of watching other people give their (mostly biased) opinions on studies and medical papers I decided to read theirs and then conduct my own experiments on myself. (Maybe inspired by Nick Norwitz, ??)
My first conclusion is that after going without sugar for 13-14 months the least little bit of sugar triggers hunger signals like I have not had in forever. As noted, I am trying to hit protein targets, and I simply can't eat that amount of meat to get to 200 grams of protein. For weight loss and using fat for energy this is a good thing. For weight/muscle gain I don't think I am fueling up as well as I need. I had some ideas and tried to kill two birds with one stone. I bought some of the pre-mixed protein drinks. I tried one, and then waited a week to try another, and then another after the third week. This container has 2.5 servings per bottle and I drank half of it and then 12 hours later the other half.
Rockin' Protein - Shamrock Farms
It has 20grams of carbohydrates and 11 grams of sugar so I'm getting them at 10 and 6 per serving.
Within an hour of each serving I am as hungry as all get out. It does not feel like an old sugar craving as I didn't really have any of those going to carnivore. But I can remember always feeling a little bit hungry. 5-6-7 20oz Mountain Dews and multiple snack cakes thru the day was providing me with the sugar to make my brain say, "I'm hungry again". I am guessing (hypothesizing if this were truly scientific) that by being off sugar/carbs for so long it only takes a very small amount to take me back to "hungry" all over again. (I have found a similar issues with seed oils. I ate them by the buckets before Carnivore and now the least little bit sends me running to the bathroom).
The sugar and the carbs have been a tradeoff for appetite and getting in extra protein. My weight fluctuates/swings normally and that has continued. Maybe up a pound or two more but swings back down to where I am averaging around 215. (still 90lbs off my start point on carnivore).
I could stand to lose some more weight, maybe 15-20lbs or so, but I am not as concerned with weight loss as of late. Super happy with the 90-95lbs in 14 months. Carnivore is still my way of eating, and as far as food is concerned it is still strict carnivore. Once a week or so I am indulging in a few carbs and a few sugars which triggers some hunger. I get the benefit of the extra protein from the drink but at the same time I can get in one more rib eye due to the hunger it provides. Probably not the best method to trigger hunger, but since I never had cravings, I don't see it being my 'gate-way' drug back to Mountain Dews and Little Debbie Snack cakes. LOL
The return? In the past month I can see a difference in my biceps and triceps. And although the aesthetics is not the goal, it is pretty cool to gain a little muscle at 55. The end goal is to gain muscle to offset the natural muscle loss from aging as well as the effects of the auto-immune disease I am trying to reverse with carnivore. The most impressive part so far is the plates I am adding in the gym. I am a lot stronger at 55 than 35. I am not 25 and just out of the service healthy but I am a lot closer to that than I was 14 months ago. And there has been some strides in the last month with "sugar dosing".
If I were struggling with weight still, I might not see this as a grand idea but since I am good with my weight right now, I don't see the harm of the occasional sugar spike. (This is similar to a four-year carnivore friend at the gym who eats sweet potatoes on Thursday nights before a big lift on Friday. Really similar concepts).
Again, not one of those double-blind studies with a thousand humans as control subjects, just me, and my approach to my own health. Maybe not the best plan, but it is my plan, and for now it is working rather well.
babbling on again.
Scott