Welcome to our Carnivore / Ketovore / Keto Online Community!
Welcome to Carnivore Talk! An online community of people who have discovered the benefits of an carnviore-centric ketogenic diet with the goal of losing weight, optimizing their health, and supporting and encouraging one another. We warmly welcome you! [Read More]
- Replies 5
- Views 749
- Created
- Last Reply
Popular Days
Most Popular Posts
-
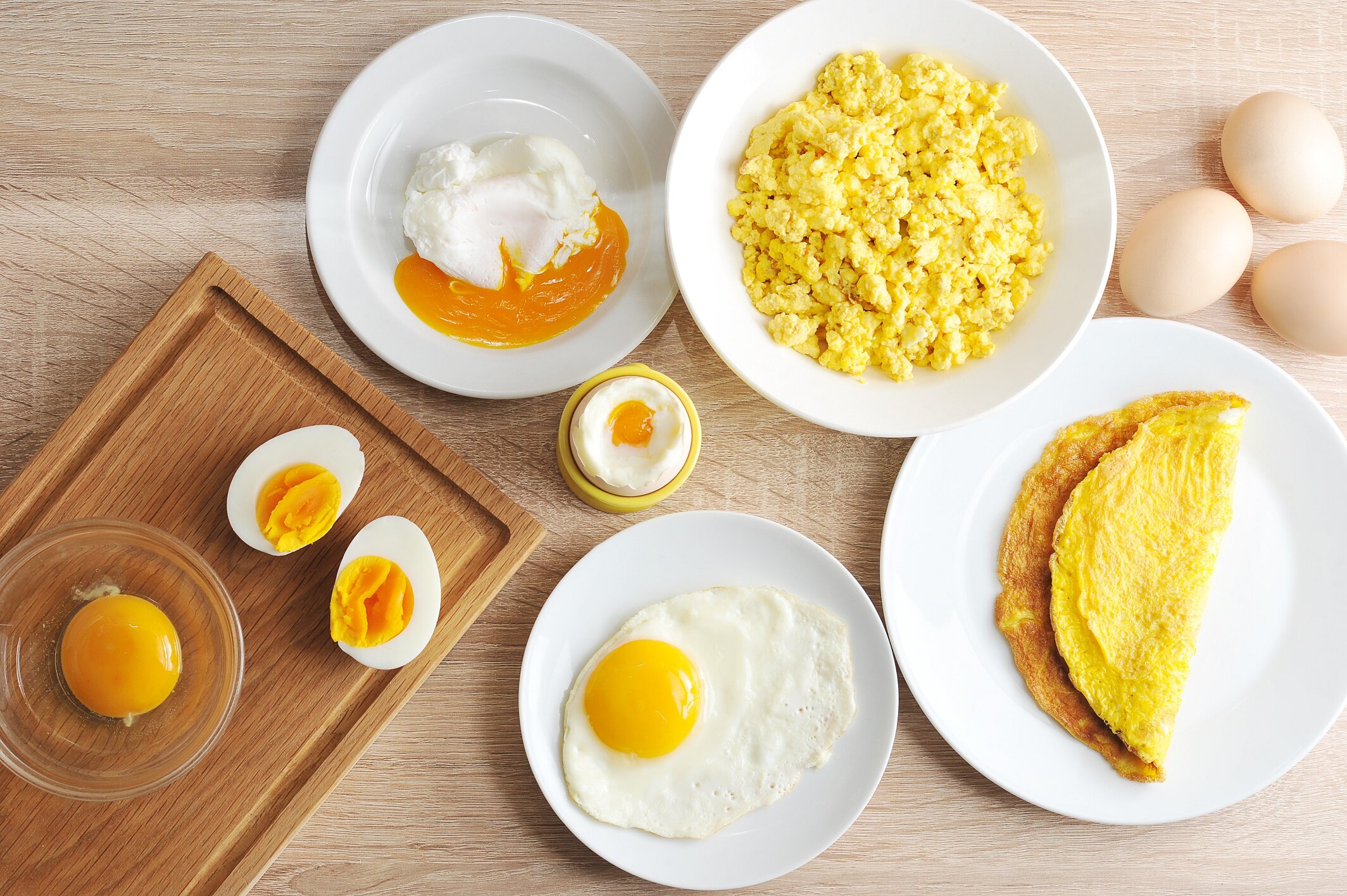
I quit using EVO because it’s hard to find any that’s not cut with canola oil. I do use some avocado oil but only to season my cast iron and my flat top. For cooking I only use butter, ghee, tallow,
-
Sort of a coincidence as today I watched several Norton videos followed by Horwitz (sp?) videos on this very subject. Although I do know what is working for me, I don't have the background nor the edu
-
I got rid of our olive oil about 3 years ago. Makes great fire pit starter fluid when mixed with a little kerosene 🤣 Now the only seed oil in our house is a small bottle of avocado oil, and I use tha








This "Healthy" Fat May Secretly Be Fueling Obesity
ScienceDaily · June 11, 2025
Olive oil's main fat may secretly drive obesity by creating more fat-storing cells. Credit: Shutterstock
Eating a high-fat diet containing a large amount of oleic acid - a type of fatty acid commonly found in olive oil - could drive obesity more than other types of dietary fats, according to a study published in the journal Cell Reports.
The study found that oleic acid, a monounsaturated fat associated with obesity, causes the body to make more fat cells. By boosting a signaling protein called AKT2 and reducing the activity of a regulating protein called LXR, high levels of oleic acid resulted in faster growth of the precursor cells that form new fat cells.
"We know that the types of fat that people eat have changed during the obesity epidemic. We wanted to know whether simply overeating a diet rich in fat causes obesity, or whether the composition of these fatty acids that make up the oils in the diet is important. Do specific fat molecules trigger responses in the cells?" said Michael Rudolph, Ph.D., assistant professor of biochemistry and physiology at the University of Oklahoma College of Medicine and member of OU Health Harold Hamm Diabetes Center.
Rudolph and his team, including Matthew Rodeheffer, Ph.D., of Yale University School of Medicine and other collaborators at Yale and New York University School of Medicine, fed mice a variety of specialized diets enriched in specific individual fatty acids, including those found in coconut oil, peanut oil, milk, lard and soybean oil. Oleic acid was the only one that caused the precursor cells that give rise to fat cells to proliferate more than other fatty acids.
"You can think of the fat cells as an army," Rudolph said. "When you give oleic acid, it initially increases the number of 'fat cell soldiers' in the army, which creates a larger capacity to store excess dietary nutrients. Over time, if the excess nutrients overtake the number of fat cells, obesity can occur, which can then lead to cardiovascular disease or diabetes if not controlled."
Unfortunately, it's not quite so easy to isolate different fatty acids in a human diet. People generally consume a complex mixture if they have cream in their coffee, a salad for lunch and meat and pasta for dinner. However, Rudolph said, there are increasing levels of oleic acid in the food supply, particularly when access to food variety is limited and fast food is an affordable option.
"I think the take-home message is moderation and to consume fats from a variety of different sources," he said. "Relatively balanced levels of oleic acid seem to be beneficial, but higher and prolonged levels may be detrimental. If someone is at risk for heart disease, high levels of oleic acid may not be a good idea."
ARTICLE SOURCE: https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2025/06/250611084111.htm
Subscribe to Carnivore Talk on YouTube | Be our guest on the channel | Leave me a voicemail, yo!